Working principle of LCD screen
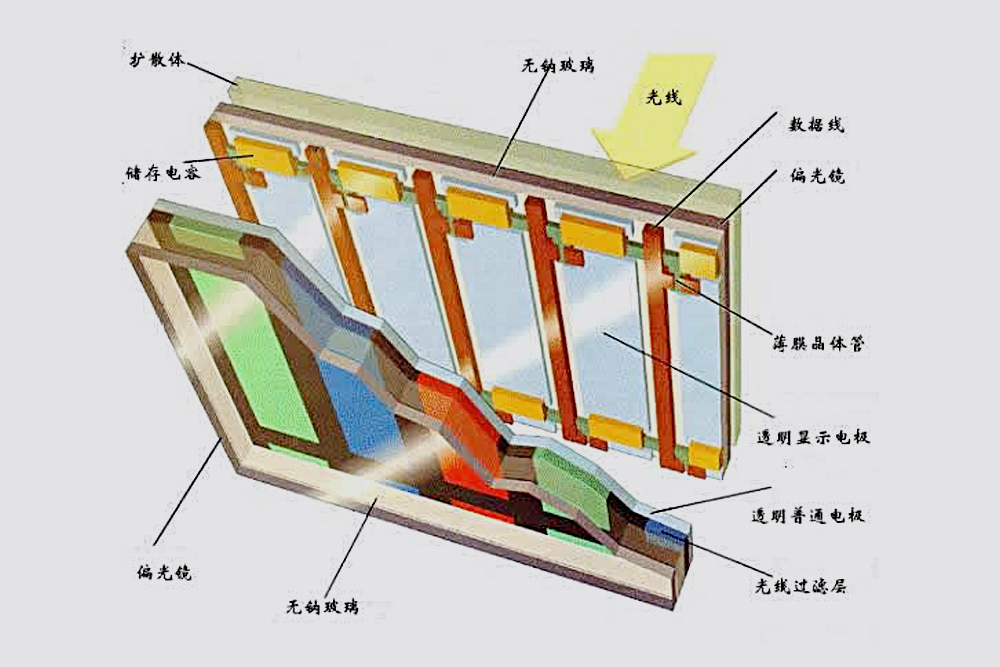
In brief, the basic principle of screen display is to fill the liquid crystal material between two parallel plates, and change the arrangement of molecules in the liquid crystal material through voltage, so as to achieve the purpose of shading and light transmission to display the images of different shades and different arrangement, and only add a ternary color filter layer between the two plates to realize the display of color images.
Only by understanding its structure and principle, and its technical and technological characteristics can it be more scientific and reasonable in application and maintenance. Liquid crystal is an organic compound composed of long rod-like molecules. In natural state, the long axis of these rod-like molecules is roughly parallel. The first feature of LCD is that the liquid crystal must be poured between two planes with slots in order to work normally. The grooves on the two planes are perpendicular to each other (90 degrees intersect), that is, if the molecules on one plane are arranged in the north-south direction, the molecules on the other plane are arranged in the east-west direction, and the molecules between the two planes are forced into a 90 degree twist state. Because the light travels along the direction of molecular arrangement, the light is also twisted 90 degrees when it passes through the liquid crystal. However, when a voltage is applied to the liquid crystal, the molecules will rearrange vertically so that the light can be directly emitted without any twist. The second characteristic of LCD is that it depends on the polarization filter and the light itself. The natural light is scattered randomly in all directions. The polarization filter is actually a series of thinner and thinner parallel lines. These lines form a net to block all rays that are not parallel to these lines. The line of the polarizing filter is just perpendicular to the first one, so it can completely block those polarized rays. Only when the lines of the two filters are completely parallel, or the light itself has been twisted to match the second polarization filter, can the light penetrate. LCD is composed of such two mutually perpendicular polarizing filters, so under normal circumstances, all light that is trying to penetrate should be blocked. However, due to the twisted liquid crystal between the two filters, after the light passes through the first filter, it will be twisted 90 degrees by the liquid crystal molecules, and finally pass through the second filter. On the other hand, if a voltage is applied to the liquid crystal, the molecules will be rearranged and completely parallel, so that the light will not be twisted, so it is just blocked by the second filter. In short, power-on will block the light, and power-on will make the light shoot out. Of course, you can also change the arrangement of the liquid crystal in the LCD so that the light is emitted when the power is on, but is blocked when the power is not on. However, since the LCD screen is almost always on, only the scheme of "power on to block the light" can achieve the goal of saving electricity.
Common classification of LCD screen
1. STN LCD screen
STN is the abbreviation of "Super Teisted Nematic". It belongs to passive matrix LCD. Almost all black and white mobile phone LCD screens are made of this material. The color STN LCD screen is to add a color filter on the basis of the monochrome STN LCD screen, and divide each pixel in the monochrome display matrix into three sub-pixels, and display red, green, and blue colors through the color filter respectively, so as to realize the color picture. Due to technical limitations, the current STN LCD screen has only 65536 colors at most. Most STN products seen on the market are 4096 colors, so STN is also known as "fake color".
2. GF LCD screen
GF is the abbreviation of "Glass Fine Color". Maybe you are unfamiliar with GF LCD, because there are very few digital products of GF LCD on the market. In fact, GF belongs to STN. The main feature of GF is that the brightness is improved under the premise of ensuring low power consumption, but the GF LCD is somewhat biased.
3. TFT LCD screen
TFT is the abbreviation of "Thin Film Transistor", also known as "True Color". It belongs to the active matrix LCD screen. It is a screen composed of thin film transistors. Each LCD pixel is driven by thin film transistors. Behind each pixel, four independent thin film transistors drive the pixel to emit color light, which can display true color of 24 bit color depth. In terms of resolution, TFT LCD can reach UXGA (1600 × 1200)。
The arrangement of TFT is memory, so it will not immediately return to its original state after the current disappears, thus improving the shortcomings of flicker and blurring of STN LCD screen, effectively improving the effect of LCD screen to display dynamic pictures, and the ability to display static pictures is also more prominent. The advantages of TFT LCD screen are short response time ratio and bright color, so it is widely used in notebook computers, DV and DC. The disadvantage of TFT LCD is that it consumes more power and costs more.
4. TFD LCD screen
TFD is the abbreviation of "Thin Film Diode". Due to the high power consumption and high cost of TFT LCD screen, which greatly increases the cost of the product, EPSON has specially developed TFD technology for mobile phone screen. It is also an active matrix LCD screen. Each pixel on the LCD is equipped with a separate diode, which can control each pixel independently, so that each pixel will not affect each other, This can significantly improve the resolution and display dynamic pictures and gorgeous colors without dragging.
In terms of performance, the TFT LCD screen takes into account the advantages of TFT LCD screen and STN LCD screen. The TFT LCD screen has higher brightness and brighter color than STN LCD screen. At the same time, it saves more power than TFT LCD screen, but it is still inferior to TFT LCD in color and brightness.
5. OLED LCD screen
OLED is the abbreviation of "Organic Light Emitting Display", also known as organic light emitting display. It uses organic light emitting technology, which is the latest display technology at present. OLED display technology is different from traditional liquid crystal display mode. It does not need backlight, but uses very thin organic material coating and glass substrate. When there is current passing through, these organic materials will emit light, so its perspective is large, The content on the screen can be seen clearly from all directions, and can be made very thin, and the OLED display can significantly save power, known as "dream display".
However, OLED is not without shortcomings. Because it is still an immature technology, its service life is relatively short and the screen area is relatively small at this stage.
Related parameters
1. Resolution
Resolution is a very important performance index. It refers to the number of points that can be displayed horizontally and vertically on the screen (the lines and faces displayed on the screen are composed of points). The higher the resolution, the more information that can be contained on the same screen. For a CRT capable of supporting 1280x1024 resolution, whether it is 320x240 or 1280x1024 resolution, it can be perfectly displayed (because the electron beam can be elastically adjusted). However, its maximum resolution is not necessarily the most appropriate resolution, because if the resolution of the 17-inch display reaches 1280x1024, the font of WINDOWS will be very small, and the eyes will be tired after a long time, so the best resolution of the 17-inch display should be 1024x768.
But not for LCD. The maximum resolution of LCD is its true resolution, which is the best resolution. Once the set resolution is less than the real resolution (for example, the real resolution of the 15-inch LCD is 1024x768, while the set resolution in WINDOWS is 800x600), there will be two display modes. The first is centered display. Only the 800x600 points in the middle of the LCD will display the image, and other unused points will not glow. Keep the dark background, and it seems that the image is centered and reduced. The other is to expand the display, which will use every pixel on the screen, but because pixels are easily distorted, it will have a certain impact on the display effect. Therefore, in any case, when selecting LCD, we should pay attention to that the resolution is not as large as possible, but is appropriate and easy to use.
2. Perspective
At present, the viewing angle of most flat panel displays can reach 180 degrees, that is, the displayed content can be clearly seen from any direction in front of the screen. LCD is different. Its visual angle varies depending on whether the technology is advanced or not. The visual angle of some new products has reached about 160 degrees, which is very close to the 180 degrees of CRT. There are also some LCDs with a nominal angle of view of 160 degrees, but they can not meet this standard. Once the user's visual angle exceeds its actual visual range during use, the color of the picture will fade, darken, or even change from a positive image to a negative image. It is likely that you will be confused by the Philips advertisement. In fact, the perspective of LCD is not very large, but much smaller than that of CRT. It is a place that is obviously weaker than CRT. So don't worry about being seen by colleagues as the pet name of the little stupid bear. Of course, it would be better if the manufacturer added technology to the product to increase the perspective. Let's introduce it.
3. Visible area
The visible area refers to the area of the screen that can be used to display images in practical applications. Because the size of CRT display is actually the size of its picture tube, the part that can be used to display the image can not reach this size at all, because the frame of the picture tube occupies part of the space. Generally speaking, the visible area of the 17-inch CRT display is about 15.8-16 inches, while the visible area of the 15-inch display is only about 13.8 inches. But for the LCD, the nominal size is basically the size of the visible area. The space occupied by the frame is very small. The visible area of the 15-inch LCD is about 14.5 inches, which is why the LCD looks larger than the CRT of the same size. So when buying LCD, 15 villages are basically enough
4. Brightness and contrast
The display function of LCD is mainly to have a backlight light source. The brightness of this light source determines the brightness and color saturation of the whole LCD. In theory, the higher the brightness of the LCD, the better. The measurement unit of brightness is cd/m2 (square candle per meter), also known as NIT lumen. At present, the brightness of TFT screen starts from 150Nits. Generally, only 200Nits can display a better picture. Contrast is the contrast measurement of different levels of black and white colors. When the contrast ratio is 120:1, vivid and rich colors can be displayed (because the human eye can distinguish the contrast ratio is about 100:1), and when the contrast ratio is up to 300:1, colors of all levels can be supported. At present, the contrast of most LCD displays is about 100:1~300:1. At present, there is no fair standard value to measure the contrast between brightness and contrast, so the purchase of LCD depends on a pair of sharp eyes. Therefore, pay attention to this indicator when selecting and purchasing LCD products. It is also the biggest difference in the performance of LCD products. It is estimated that there is some difficulty in selecting and purchasing LCD products.
5. Reaction speed
The time unit for measuring reaction speed is millisecond (ms), which refers to the time required for pixels to turn from light to dark and from dark to two. The smaller the value, the better. The smaller the value, the faster the reaction speed. At present, the response speed of mainstream LCD is more than 25ms. It doesn't matter much in general commercial applications (such as word processing or text processing), because such applications don't need to pay much attention to the response time of LCD. When it is used to play games, watch full-screen high-speed dynamic images such as VCD/DVD, the reaction time is particularly important. If the reaction time is longer, the picture will appear tail dragging, shadow and other phenomena. For a simple example, most LCD monitors in the market now have different degrees of tailing when playing QUAKE3, especially when the picture is updated at high speed. However, CRT has no such problem at all, because the reaction time of CRT is only 1ms, and there is absolutely no tailing phenomenon.
6. Color
When it comes to color, LCD can't compare with CRT. In theory, CRT can display unlimited colors just like TV. While LCD can only display about 260000 colors, most products claim to be able to display 16.77 million colors (16777216 colors, 32 bits), but they are actually achieved by dithering algorithm. Compared with the real 32 bits color, there is still a big gap, so the color expression and transition are still inferior to traditional CRT. In the same way, LCD is not as good as CRT in displaying gray scale. If you have conditions, you can compare it by yourself: find a display of a 17-inch Teletron picture tube, put a 15-inch LCD, and display a 16.77 million color image at the same time. The picture displayed by CRT is very bright, while the LCD is somewhat "fake". Although there is nothing wrong with it, it is not as comfortable as the long CRT.
LCD screen protection
We talked about the protective film of the screen. We suggest that you stick it on when you don't use the LCD screen and remove it when you use the LCD screen. This can effectively protect the chemical coating on the outer layer of the screen, so that the outermost coating will not be oxidized prematurely. In the process of using the notebook computer, users should not easily use their hands to point/press the LCD screen, or use hard objects to contact the screen. If you often do not pay attention to it for a long time, there will be scars on the LCD screen, such as white print, which will never be erased, and then you will regret it. A layer of cotton paper is usually included in the packaging of the new machine. You can also put this layer of cotton paper between the screen and keyboard of the notebook computer to reduce the wear between the screen and the hard hat. If your laptop uses a pointer, we also recommend that you take off the pointer cap and store it separately when you take your laptop out for a long time to avoid screen injury
Moisture is the "natural enemy" of the LCD screen. In addition to avoiding drinking drinks and eating fruits at the edge of the LCD screen as much as possible, you should also pay attention not to store the machine in a damp place, because serious moisture will damage the components inside the LCD screen. It is particularly noteworthy that in winter and summer, when entering and leaving a room with heating or air conditioning, a large temperature difference will also lead to "condensation". At this time, users may also cause LCD electrode corrosion and permanent damage by powering on the LCD. For this reason, we also recommend that your ambient temperature change should not be greater than 10 ℃/10min. In case of water ingress on the screen, if you only find that there is fog on the screen surface before starting the machine, gently wipe it off with a soft cloth and then start the machine again. If water has entered the LCD, the LCD should be placed in a warmer place, such as under a desk lamp, to gradually evaporate the water inside. In the plum rain season, we should also pay attention to running the LCD screen for a period of time regularly, so that the heating elements can disperse the moisture. It is better to put a small bag of moisture-proof agent in the bag containing the LCD screen to create a good home for the beloved machine.
For screen maintenance, in addition to paying attention to the above problems, you can also use soft or manual cooperation. Because the life of LCD screen is much shorter than CRT, and its aging speed is much faster, we need to pay special attention to it when we use it normally. For example, in the field of power management
